Potential Problem Areas widget
What is the Potential Problem Areas widget?
Who can access the Potential Problem Areas widget?
You do not require a license to access the Points tab of the widget, unless you use an Open Application Server (OAS). For an OAS, you require the Metasys Potential Problem Areas license to access Potential Problem Areas Points. The widget itself may additionally include two separate licensable features, namely Fault Detection and Fault Triage. You require the Metasys Fault Detection and the Metasys Fault Triage licenses to access both Fault Detection and Fault Triage. You can use Fault Detection without a Fault Triage license, but you require both licenses for Fault Detection and Fault Triage to use Fault Triage.
| License | Feature availability and behavior | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potential Problem Areas | Fault Detect-ion | Fault Triage | Potential Problem Areas widget | Points tab | Faults tab | Fault list order and catego-rization | Worst fault rollup | Fault sup-pression | Fault occur-rence | Fault duration | Fault Triage | Fault Manager |
| No1 | No | No |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| No | No | Yes |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| No | Yes | No |  2 2 |
 |
 |
S3 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| No | Yes | Yes |  2 2 |
 |
 |
S, O, D4 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Yes5 | No | No |  6 6 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Yes | No | Yes |  6 6 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Yes | Yes | No |  |
 |
 |
S 3 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |  |
 |
 |
S, O, D 4 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
How do I access the Potential Problem Areas widget?
You can find the Potential Problem Areas widget on any Space dashboard.
What is the layout of the Potential Problem Areas widget?
The following figures and tables describe the layout of the Potential Problems Areas widget when all features are licensed. See Table 1 for more details.
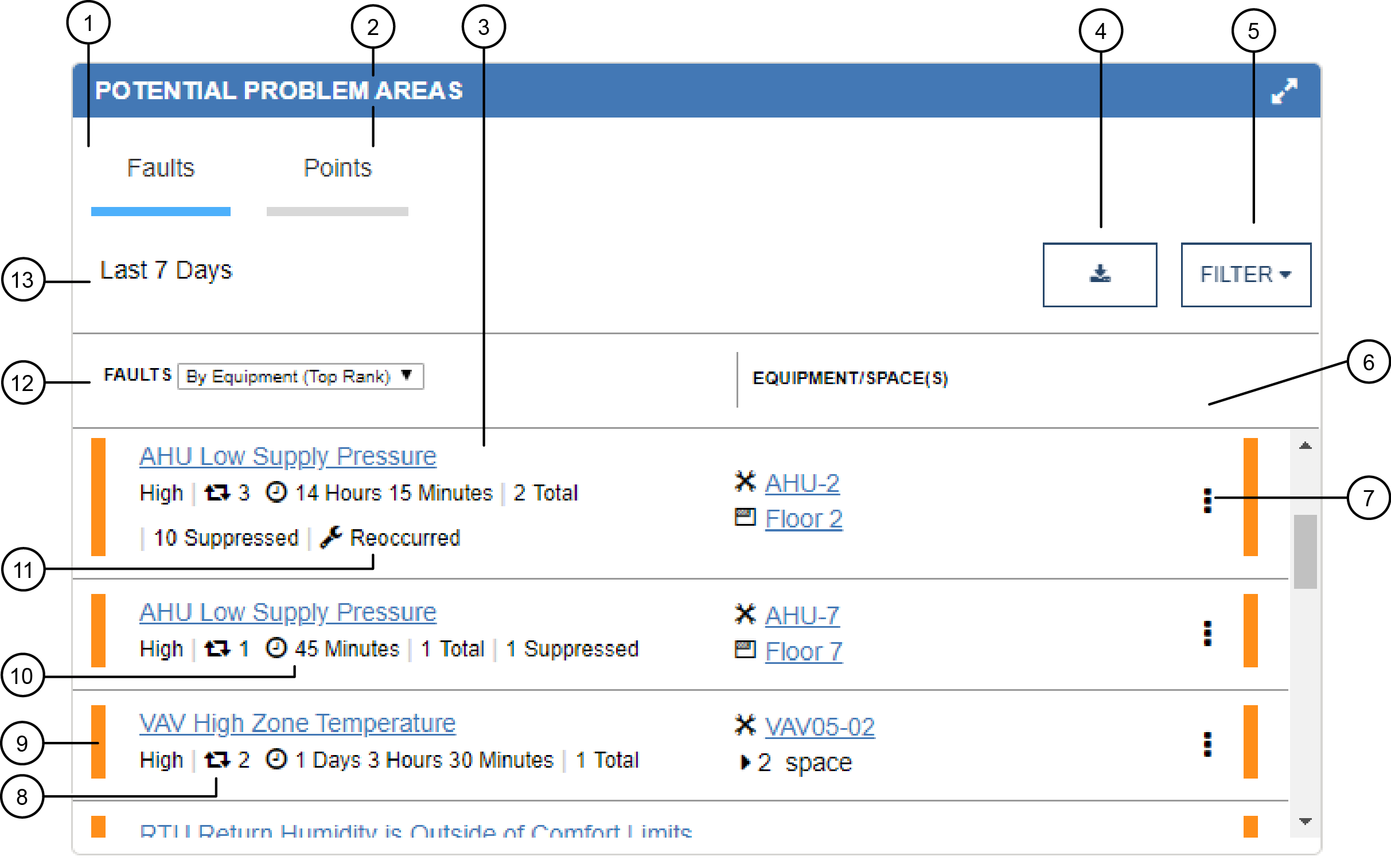
|
Number |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Faults tab |
This tab displays only if you have the Potential Problem Areas (license required on OAS only) and the Fault Detection license. When Fault Detection is licensed, then this is the default tab. It shows a detailed list of faults. |
|
2 |
Points tab |
This tab displays only if you have the Potential Problem Areas (license required on OAS only) and the Fault Detection license. View a list of any points within the space that is not operating appropriately. See Figure 2 for more information. |
|
3 |
Fault |
If Fault Detection is licensed, you see the
following information:
You can see additional information when Fault Triage is also licensed:
|
|
4 |
Export button |
Exports the fault data in the Potential Problem Areas widget to a .csv file. Note: The export functionality is not supported
on tablets or smartphones.
|
|
5 |
Filter |
Determines the faults that appear in the widget. You can filter the faults by severity or rank, such as Critical, High, Medium, and Low. You can also filter the faults by fault types, such as AHU, VAV, FCU, RTU, and Suppressed Faults. Note: In certain cases, when you filter for High and Low faults,
you may not get results for Low faults, due to the worst
fault roll up functionality.
See also How does the Suppressed Faults filter in the Faults tab work? for more information about filtering for suppressed faults. |
|
6 |
Equipment/ Spaces(s) |
Shows the equipment and the spaces that are affected by the fault. The hyperlink takes you to the equipment or space. |
|
7 |
Disable menu | This icon displays
for Administrator users only. Administrator users can click this
icon to display a menu and choose between the following disable
options:
Note: When you disable a fault rule for all
equipment, the rule is disabled, but the exceptions table in
the Fault Manager does not list the equipment for which the
rule is disabled. |
|
8 |
Occurrence icon |
Shows the number of times that this fault has occurred within the last seven days. |
|
9 |
Fault categorization bar |
Shows the categorization of a fault: critical fault = red, high fault = orange, medium fault = yellow, low fault = gray. |
|
10 |
Duration icon |
Shows the total duration of all occurrences of the fault within the last seven days. |
|
11 |
Status icon |
Shows if work on this issue is in progress, or if the fault has reoccurred. |
|
12 |
Faults drop-down menu |
The default option By Equipment (Top Severity) or By Equipment (Top Rank) displays a compressed list of faults. Only the worst fault is displayed in the list for each equipment and additional faults can be viewed by hovering over Total. Select All (Severity) or All (Ranked) to see the expanded list, which includes multiple faults for the same equipment. |
|
13 |
Fault time frame |
Displays the time frame for which the faults in the list are reporting about. The default time frame is Last 7 Days. |
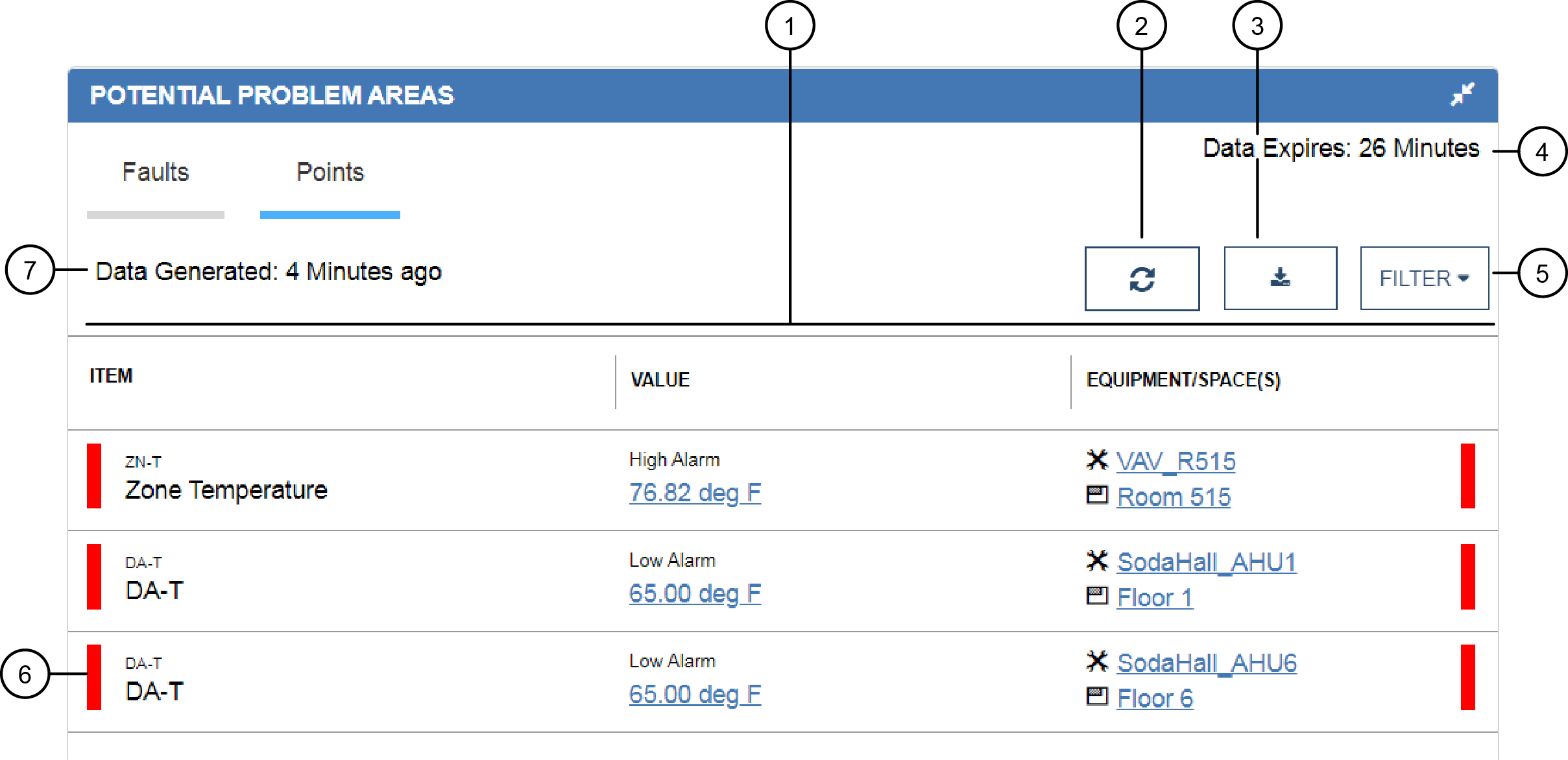
|
Number |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Data columns |
Shows the following:
|
|
2 |
Refresh button | The points are on a refresh cycle that lasts approximately 30 minutes. When this cycle expires, a Refresh button displays next to the Export button. Click or tap the Refresh button to display the updated data. You can also refresh the browser to display the updated data. |
|
3 |
Export button |
Exports the point's data in the Potential Problem Areas widget to a .csv file. Note: The export functionality is not supported on
tablets or smartphones.
|
|
4 |
Data expires timer |
Indicates when the report of points data expires. The report of data expires approximately every 30 minutes. If the report data has expired (as seen by 0 minutes), you can refresh the data by clicking or tapping the refresh button. |
|
5 |
Filter |
Determines the point statuses that appear in the widget. You can filter the points by Above Setpoint, Alarm, Below Setpoint, Offline, Out of Service, Overridden, Trouble/Warning, and Value Inaccessible. |
|
6 |
Status bar |
Shows the status of the point using the Metasys system preference colors. |
|
7 |
Data generated timer |
The data displayed in this view does not automatically refresh. This timer indicates when this report of data was taken. See also the entries in this table for Refresh button and Data expires timer. |
What information appears for each point?
The following information appears for each point that is in a status other than normal.
- Point status (listed under the Item column along with the associated color bar)
- Point short name and long name (listed under the Item column)
- Points that are Offline will show the last value that was stored within the previous seven days. If no values were stored within that time frame, no value will be shown.
- Equipment that contains the point
- Spaces that are served by this equipment
How current is the data in the Faults tab?
The system gathers data and creates faults approximately every 60 minutes on the hour, but in the Potential Problem Areas widget you only see the faults at the time of page load. You can refresh the browser to display the updated data. This action refreshes the list after the next periodic event has occurred.
How current is the data in the Points tab?
The data is a report (also known as a snapshot). A date and time stamp shows the last time the report of data was updated. The points are on a refresh cycle that lasts approximately 30 minutes. When this cycle expires, a Refresh button displays next to the Export button in the Points tab of the Potential Problem Areas widget. Click or tap the Refresh button to display the updated data. You can also refresh the browser to display the updated data.
Can I sort the data?
In the Points tab you can sort the columns in ascending or descending alphanumeric order by tapping or clicking the column header. Sorting applies to all pages of data and not just the current page. You cannot sort the data in the Faults tab, because the fault list order is intended to drive the worst faults to the top of the list. You can modify the fault list with filters only.
Why don't I see any faults?
There can be several reasons why you may not see any faults. First, make sure that all criteria are met for a given fault. When no faults occur, it is likely that a short name was not properly mapped to its semantic data point model. If your site uses point names that deviate from the Johnson Controls standard, you may need to use the Point Setting file in SCT to configure your point short names. See the Updating point settings section in System Configuration Tool Help (LIT-12011964) for more information.
What is fault suppression?
| Suppressing fault rules | Suppressed fault rules | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAV Insufficient Heating Capacity | VAV Insufficient Flow Capacity | VAV Low Zone Temperature | VAV High Zone Temperature | VAV High Flow | VAV Low Flow | VAV Zone CO2 Level is Too High | VAV Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | |
| AHU Insufficient Heating Capacity | YES | - | YES | - | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU Not Running when Occupied | - | YES | - | - | - | YES | - | YES |
| AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Closed | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES | - |
| AHU High Supply Pressure | YES | - | YES | - | YES | - | - | - |
| AHU Insufficient Fan Capacity | - | YES | - | YES | - | YES | YES | YES |
| AHU Zone CO2 Level is Too High | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES | - |
| AHU Low Supply Pressure | - | YES | - | YES | - | YES | YES | YES |
| AHU Low Discharge Air Temperature | YES | - | YES | - | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU High Discharge Air Temperature | - | - | - | YES | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES | - |
| AHU Return CO2 Level is Too High | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES | - |
| AHU Low Return Air Temperature | YES | - | YES | - | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU High Return Air Temperature | - | - | - | YES | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES |
| AHU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES |
How does the Suppressed Faults filter in the Faults tab work?
| Filters | Displayed faults | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHU | VAV | Critical | High | Medium | Low | Suppressed Faults | |
| Selected | - | - | - | - | - | Selected | AHU faults and suppressed VAV faults |
| - | Selected | - | - | - | - | Selected | VAV faults and suppressed VAV faults |
| - | - | Selected | - | - | - | Selected | All faults, including suppressed, that are critical |
| - | - | Selected | - | - | Selected | All faults, including suppressed, that are high | |
| - | - | - | - | Selected | - | Selected | All faults, including suppressed, that are medium |
| - | - | - | - | - | Selected | Selected | All faults, including suppressed, that are low |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Any non-suppressed faults that match other selected filters, such as FCU and RTU |
What does it mean when a point has a status of Value Inaccessible or Value Cannot be Read?
If an online point has a status of Value Inaccessible or
Value Cannot be Read, the Metasys UI is unable to gain
access to the point. If the point is offline, it shows an Offline status.
Value Inaccessible or Value Cannot be
Read.How do I export the data in the Potential Problem Areas widget?
You can export the fault's data and the point's data separately in the Potential Problem Areas widget to a .csv file. Simply click the Export button in the upper-right corner of the screen on both the Faults tab and the Points tab.
Is the Potential Problem Areas widget supported on all devices?
Yes, the Potential Problem Areas widget is supported on desktop, tablets, and smartphones.
What is Fault Triage?
Fault Triage provides a unique view, which provides additional information on a particular fault, corrective actions in the order of their likeliness to resolve the issue, a description of the fault, charting of supporting data, and an activity log to track progress. Fault Triage also enhances the sorting order and information in the Faults tab of the Potential Problem Areas widget to introduce fault occurrences and durations to better drive the most problematic issues to the top of the list.
Who can access Fault Triage?
You require both the Metasys Fault Detection and the Metasys Fault Triage license to access the feature.
How can I access Fault Triage?
- Navigate to the Potential Problem Areas widget on the Space dashboard.
- In the Faults tab, click or tap the hyperlinked fault that you want to investigate.
- The Fault Triage window opens in a new tab.
What is the layout of the Fault Triage window?
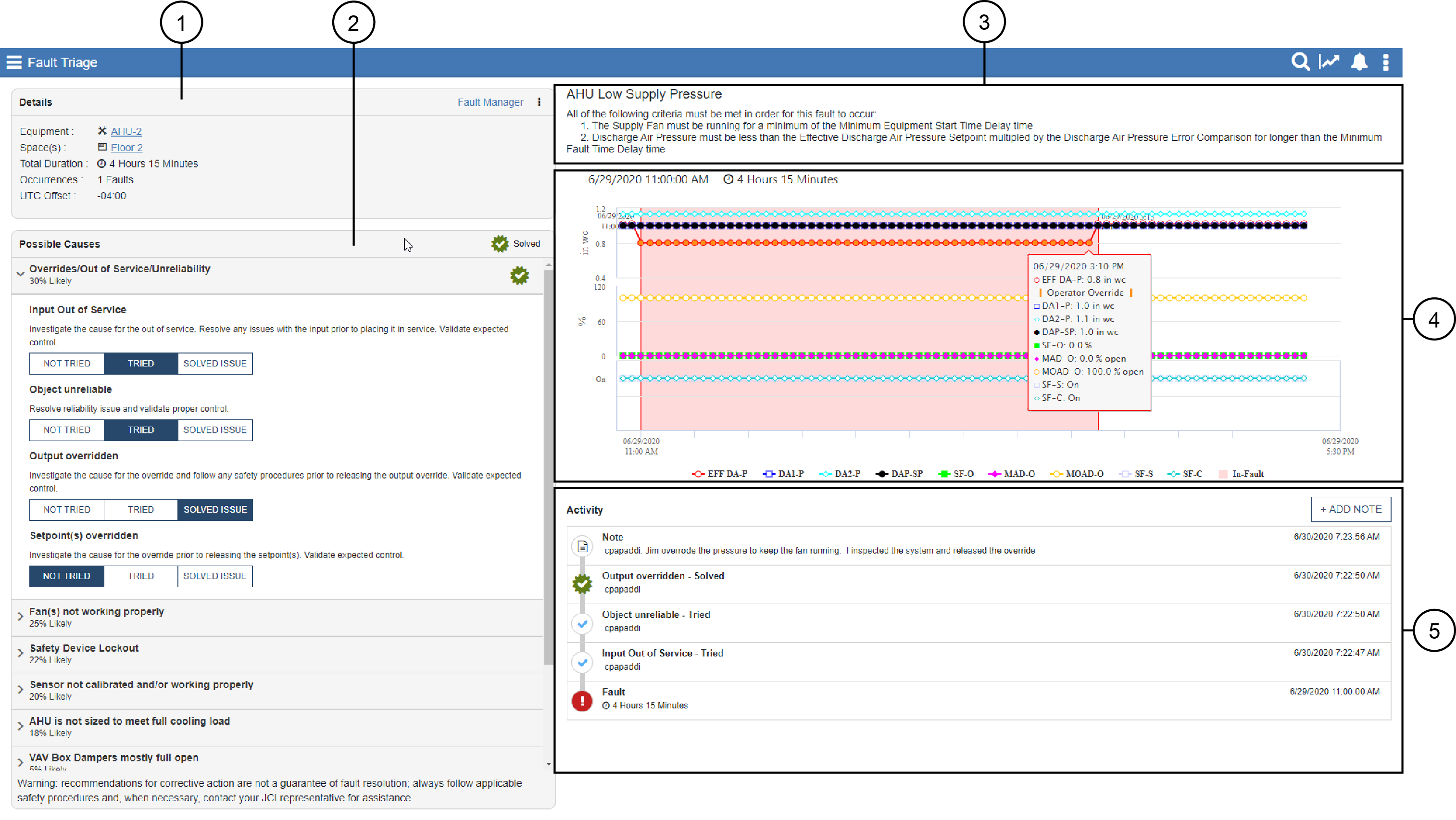
|
Number |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Details |
This section shows the affected equipment and spaces served by the equipment, including hyperlinks to the relevant equipment and space(s). It also shows the total duration of all fault occurrences within the previous seven days, and the total occurrences of the fault within the previous seven days. As an Administrator user, you can also access the Fault Manager from the Details section. See What is the Fault Manager? for more information about viewing fault rules, managing global attributes, and using the Import and Export feature. As an Administrator user, you can click or tap the Disable menu (three vertical dots) to display a menu, which gives you the ability to disable this fault rule for this equipment, disable all fault rules for this equipment, and disable this fault rule for all equipment. Note: When you disable a fault rule for all
equipment, the rule is disabled, but the exceptions table in
the Fault Manager does not list the equipment for which the
rule is disabled.
|
|
2 |
Possible Causes |
Any given fault can occur as a result of a
number of given root causes. A group of a half dozen Johnson
Controls HVAC Controls technical experts from across North
America with a combined experience of over 150 years provided
the following input for the Fault Triage feature:
See How do I take action on a fault? for more information. |
|
3 |
Fault Name and Description |
This section shows you the fault name and the criteria that must be met for the fault to occur. See What types of fault rules are there? What data is required for each fault to occur? for a list of all fault names and corresponding criteria. See also How do I modify fault rule attributes in the Fault Manager? to learn more about changing global attributes. |
|
4 |
Charting |
This is an auto-generated chart that is provided with each fault occurrence. The chart displays pertinent data before, during, and after the fault occurs. Use the arrow buttons to see data from each fault occurrence. The first page displays the most recent fault. Stacked charting provides the following information, as appropriate:
Note: Line marker fill colors are colored to indicate non-normal
status. Tool tips provide a list of all the data at that
point in time. You can hide or unhide individual data
points.
See What information is provided in the Fault Triage trend charts for each fault? and How does Fault Triage charting differ from Trends or from a Trend Study? for more information. |
|
5 |
Activity |
This log shows the fault occurrences, including the date and time it first occurred, along with the fault duration of that occurrence. The log also shows the corrective action progress, as any corrective action marked TRIED or SOLVED ISSUE appears with the user name and time stamp. You can also see user notes, which can give you more information about an issue and corrective actions. Click +ADD NOTE to add a user note. Note: The Equipment Activity widget and System
Activity do not display activity items for faults.
|
How do I take action on a fault?
- Click or tap on a fault listed in the Potential Problem Areas widget. The Fault Triage window opens in a new tab.
- In the Fault Triage window, navigate to the Possible Causes section.
- Expand the possible causes to see further causes and suggested corrective actions.
- Try the corrective actions as appropriate.
- Click or tap NOT TRIED, TRIED, and SOLVED ISSUE to log your action. The action log displays in the Activity section in the lower right of your screen.
- It is also best practice to add a note in the Activity log, especially when the possible cause was Other.
For example, the fault AHU Low Discharge Air Temperature can be caused by Heating is not working properly, and that in turn can be caused by Dirty coil (exterior). Fault Triage suggests to Clean exterior of coil to rated pressure drop. If you believe this to have been the root cause of the fault then mark the solution with SOLVED ISSUE. The selection persists until the fault reoccurs, but the instance of the fault is removed from the list after seven days. If indeed cleaning the coil was not the root cause, or if other factors were involved, the fault will reappear in the fault list within seven days after being marked solved with a status of Reoccurred. The previous selections on other root causes will be persisted and the Clean exterior of coil to rated pressure drop selection will be automatically marked as TRIED.
What is the Fault Manager?
The Fault Manager is closely linked to Fault Triage. You can view, enable, and disable all fault rules in the Fault Manager. You can modify global attributes and you can also download an archive of global attributes, exceptions, and activity logs, and you can import an archive to restore data from a previous archive.
Who can access the Fault Manager?
Only Administrator users can access the Fault Manager. You also require the Metasys Fault Detection license to access the Fault Manager.
How can I access the Fault Manager?
- Open the User menu.
- Tap or click Administrative Tasks.
- Tap or click Fault Manager.
You can also access the Fault Manager in the Details section of the Fault Triage window.
What is fault severity and how is it used?
To find out about fault severity go to the Fault Manager first, as the Fault Manager lists the fault rules based on severity. The worst faults are at the top of the list, while minor faults, such as energy saving opportunities, are listed towards the bottom of the list.
The order of the faults in the Faults tab of the Potential Problem Areas widget is also by severity, if Fault Triage is not licensed. When Fault Triage is licensed, the fault duration and occurrences are also factored into the order of the faults displayed in the Faults tab of the Potential Problem Areas widget.
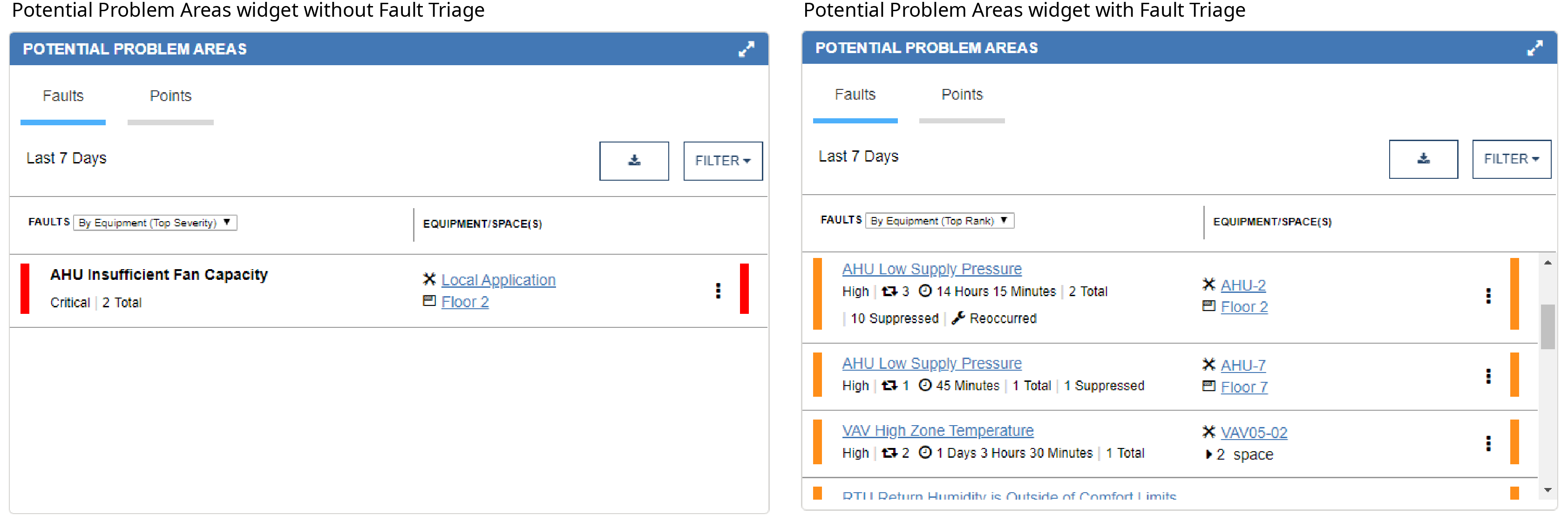
| Rule | Severity | Color | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Open | Critical | Red |
| 2 | AHU Insufficient Heating Capacity | ||
| 3 | AHU Not Running when Occupied | ||
| 4 | AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Closed | ||
| 5 | AHU High Supply Pressure | ||
| 6 | AHU Insufficient Fan Capacity | ||
| 7 | AHU Zone CO2 Level is Too High | High | Orange |
| 8 | AHU Low Supply Pressure | ||
| 9 | AHU Low Discharge Air Temperature | ||
| 10 | AHU High Discharge Air Temperature | ||
| 11 | AHU Building Static Pressure is Too Low | ||
| 12 | AHU Building Static Pressure is Too High | ||
| 13 | AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too Low | ||
| 14 | AHU Return CO2 Level is Too High | ||
| 15 | AHU Low Return Air Temperature | ||
| 16 | AHU Low Zone Temperature | ||
| 17 | AHU High Return Air Temperature | ||
| 18 | AHU High Zone Temperature | ||
| 19 | AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too High | ||
| 20 | AHU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 21 | AHU Return Humidity Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 22 | RTU Insufficient Heating Capacity | ||
| 23 | RTU Not Running when Occupied | ||
| 24 | RTU Zone CO2 Level is Too High | ||
| 25 | RTU Low Discharge Air Temperature | ||
| 26 | RTU High Discharge Air Temperature | ||
| 27 | RTU Return CO2 Level is Too High | ||
| 28 | RTU Low Return Air Temperature | Medium | Yellow |
| 29 | RTU High Return Air Temperature | ||
| 30 | RTU Low Zone Temperature | ||
| 31 | RTU High Zone Temperature | ||
| 32 | RTU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 33 | RTU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 34 | FCU Insufficient Heating Capacity | ||
| 35 | FCU Low Zone Temperature | ||
| 36 | FCU High Zone Temperature | ||
| 37 | VAV Insufficient Heating Capacity | ||
| 38 | VAV Insufficient Flow Capacity | ||
| 39 | VAV Low Zone Temperature | ||
| 40 | VAV High Zone Temperature | ||
| 41 | VAV High Flow | ||
| 42 | VAV Low Flow | ||
| 43 | VAV Zone CO2 Level is Too High | ||
| 44 | VAV Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 45 | AHU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits | Low | Gray |
| 46 | AHU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer | ||
| 47 | AHU Constantly Running | ||
| 48 | AHU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 49 | AHU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 50 | AHU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low | ||
| 51 | AHU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low | ||
| 52 | RTU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits | ||
| 53 | RTU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer | ||
| 54 | RTU Constantly Running | ||
| 55 | RTU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 56 | RTU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low | ||
| 57 | RTU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 58 | RTU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low | ||
| 59 | FCU Simultaneously Heating and Cooling | ||
| 60 | FCU Heating or Cooling While a Window is Open | ||
| 61 | FCU A Window is Open While Unoccupied | ||
| 62 | FCU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 63 | FCU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low | ||
| 64 | VAV Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High | ||
| 65 | VAV Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
How do I learn more about a fault rule and its exceptions in the Fault Manager?
- Click or tap on a fault rule listed in the FAULT RULES column. The FAULT RULE window opens.
- Review the details about what triggers this rule, the
attributes of the rule, and the exceptions of the rule. Note: An exception is a piece of equipment for which a rule is disabled.
How can I turn a fault rule on or off?
This can be done in multiple ways:
- With the Disable menu (three vertical dots), which is displayed next to a Fault in the Potential Problem Areas widget Faults tab, if you are logged in as an Administrator user.
- With the Disable menu (three vertical dots), which is displayed in the Details section of Fault Triage, if you are logged in as an Administrator user.
- With the ENABLE/DISABLE toggles in the Fault Manager. You can perform this action on a rule-by-rule basis, or in bulk by using the toggle in the header.
- With the ENABLE/DISABLE toggle in the FAULT RULE window in the Fault Manager.
How do I enable exceptions (equipment that has been disabled) in the Fault Manager?
- Click or tap on a fault rule listed in the FAULT RULES column. The FAULT RULE window opens.
- Navigate to the exceptions table at the bottom of the window.
- Select the equipment that you want to enable the fault for.
- Click or tap the toggle in the ENABLE/DISABLE column as appropriate.
- Click SAVE to save your changes.
How do I filter fault rules in the Fault Manager?
- Click or tap FILTER in the upper-right corner of the screen.
- Select the equipment type(s) that you want to filter for.
How do I modify fault rule attributes in the Fault Manager?
- Click or tap GLOBAL ATTRIBUTES in the upper-right corner of the screen. The GLOBAL ATTRIBUTES SETTINGS window opens.
- Hover your cursor over the attribute to see a description of the attribute.
- Hover your cursor over the faults data in the ASSIGNED TO column to check the fault rules
that this attribute relates to. Important: Changes to an attribute affect all assigned to fault rules.
- Change the value in the VALUE column.
- Click or tap SAVE
to keep and save your changes. Note: Click or tap RESET VALUES to revert your changes to the default values. The default values take into account rounding and calibration values typically found in the field.
How can I back up the changes I make in the Fault Manager?
- Click ARCHIVE in the upper-right corner of the Fault Manger. The ARCHIVE window opens.
- Click EXPORT to download the .archive file.
How do I import backed up Fault Manager data?
- Click ARCHIVE in the upper-right corner of the Fault Manger. The ARCHIVE window opens.
- Click Choose File and select the .archive file you want to import.
- Click IMPORT.
What is the difference between a Metasys alarm and a Metasys fault?
Alarm: Alarm extensions provide a way to notify a user when system points exceed configured thresholds. You can manually enter thresholds or you can base the thresholds on an additional point, such as a control setpoint. The thresholds can also include reporting delays. The Alarm Manager handles management of alarms, including acknowledgment, discards, and annotations.
Fault: Faults can utilize more system points, delays, and thresholds that are directly related to each individual fault. Faults are not included in Alarm Management, but in the Potential Problem Areas widget.
| Aspects | Alarm | Fault |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Finite data, thresholds, and delays | Expanded and focused data, thresholds, and delays |
| Sample time | Exact | Binning: all data samples are put in five minute bins. For example, if a fault occurs at 12:03 it is registered in the 12:00 bin. |
| Detection frequency | Immediately annunciated by the event | Events are evaluated at fixed intervals. Faults are evaluated at fixed intervals. |
| Notification | Immediate through the alarm icon and entry in Alarm Manager or Alarm Monitor | Fixed interval on Potential Problem Areas widget Faults tab, rolling seven days |
| Prioritization | Alarm priority | Fault severity, Fault rank |
| Management | Alarm Manager: acknowledge, discard, or annotate alarms |
|
Although alarms and faults are similar, faults provide a "smarter" indication of building system issues. Utilizing both faults and alarms within your Metasys system can increase productivity and greatly minimize nuisance problem reporting. A fault can help you determine if an alarm is justified. You can use the fault findings to fine tune the alarm settings. When you manage a site, consider looking more closely at faults and reserve alarms for reporting issues that are truly alarming.
For example, regarding a temperature threshold, you can eliminate nuisance and spurious alarms by using faults to determine if a piece of equipment is still failing to achieve setpoint after it has had time to ramp up to a stable state. You can then create alarms for the space, which detect real emergencies.
What types of fault rules are there? What data is required for each fault to occur?
| Fault Rule | All of the following criteria must be met in order for the respective fault to occur7 | Required semantic point model |
|---|---|---|
| AHU Building Static Pressure is Too High |
|
|
| AHU Building Static Pressure is Too Low |
|
|
| AHU Constantly Running | This fault occurs any time that the Supply Fan is running for longer than the Equipment Excessive Runtime time. It is intended to identify systems which should be shutting down and not doing so. Disable this fault for any systems which must always run. |
|
| AHU High Discharge Air Temperature8 |
|
|
| AHU High Return Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| AHU High Supply Pressure |
|
|
| AHU High Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| AHU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| AHU Insufficient Fan Capacity |
|
|
| AHU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
| AHU Low Discharge Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| AHU Low Return Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| AHU Low Supply Pressure |
|
|
| AHU Low Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| AHU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer |
|
|
| AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Closed |
|
|
| AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Open |
|
|
| AHU Not Running when Occupied |
|
|
| AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too High |
|
|
| AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too Low |
|
|
| AHU Return CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
| AHU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| AHU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Return Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| AHU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Return Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
| AHU Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
| AHU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| AHU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Zone Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| AHU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Zone Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
| FCU A Window is Open While Unoccupied |
|
|
| FCU Heating or Cooling While a Window is Open |
|
|
| FCU High Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| FCU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
| FCU Low Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| FCU Simultaneously Heating and Cooling |
|
|
| FCU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Zone Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| FCU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Zone Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
| RTU Constantly Running | This fault occurs any time that the Supply Fan is running for longer than the Equipment Excessive Runtime time. It is intended to identify systems which should be shutting down and not doing so. Disable this fault for any systems which must always run. |
|
| RTU High Discharge Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU High Return Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU High Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits | Any of the
following criteria must be met in order for this fault to occur:
|
|
| RTU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
| RTU Low Discharge Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU Low Return Air Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU Low Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| RTU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer |
|
|
| RTU Not Running when Occupied |
|
|
| RTU Return CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
| RTU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| RTU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Return Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| RTU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Return Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
| RTU Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
| RTU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| RTU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Zone Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| RTU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Zone Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
| VAV High Flow |
|
|
| VAV High Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| VAV Insufficient Flow Capacity |
|
|
| VAV Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
| VAV Low Flow |
|
|
| VAV Low Zone Temperature 8 |
|
|
| VAV Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
| VAV Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
| VAV Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Cooling Temperature Setpoint is below the Zone Temperature Setpoint Minimum attribute. |
|
| VAV Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High 8 | This fault occurs any time that the Effective Heating Temperature Setpoint is above the Zone Temperature Setpoint Maximum attribute. |
|
You can see these fault rules and their descriptions in the Fault Manager, when you click on an individual fault rule; and in the Charting section in the upper right of the Fault Triage window.
What equipment can return a fault?
| General fault type | VAV | FCU | RTU | AHU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Open |  |
|||
| Insufficient Heating Capacity |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Not Running when Occupied |  |
 |
||
| Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Closed |  |
|||
| High Supply Pressure |  |
|||
| Insufficient Fan Capacity |  |
|||
| Zone CO2 Level is Too High |  |
 |
 |
|
| Low Supply Pressure |  |
|||
| Low Discharge Air Temperature |  |
 |
||
| High Discharge Air Temperature |  |
 |
||
| Building Static Pressure is Too Low |  |
|||
| Building Static Pressure is Too High |  |
|||
| Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too Low |  |
|||
| Return CO2 Level is Too High |  |
 |
||
| Low Return Air Temperature |  |
 |
||
| Low Zone Temperature |  |
 |
 |
 |
| High Return Air Temperature |  |
 |
||
| High Zone Temperature |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |  |
 |
||
| Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |  |
 |
||
| Humidity Setpoint Outside of Comfort Limits |  |
 |
 |
|
| Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too High |  |
|||
| Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |  |
 |
||
| Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |  |
 |
||
| Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Insufficient Flow Capacity |  |
|||
| High Flow |  |
|||
| Low Flow |  |
|||
| Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer |  |
 |
||
| Constantly Running |  |
 |
||
| Simultaneously Heating and Cooling |  |
|||
| Heating or Cooling While a Window is Open |  |
|||
| A Window is Open While Unoccupied |  |
|||
| Number of faults for each equipment type | 10 | 8 | 19 | 28 |
What information is provided in the Fault Triage trend charts for each fault?
| Fault rule | Top chart | Middle chart | Bottom chart |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHU Building Static Pressure is Too High |
|
|
|
| AHU Building Static Pressure is Too Low |
|
|
|
| AHU Constantly Running | not applicable | not applicable |
|
| AHU High Discharge Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU High Return Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU High Supply Pressure |
|
|
|
| AHU High Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
not applicable | not applicable |
| AHU Insufficient Fan Capacity |
|
|
|
| AHU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
|
| AHU Low Discharge Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU Low Return Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU Low Supply Pressure |
|
|
|
| AHU Low Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| AHU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer |
|
|
|
| AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Closed |
|
|
|
| AHU Mixed Air Dampers are Stuck Open |
|
|
|
| AHU Not Running when Occupied | not applicable | not applicable |
|
| AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too High |
|
|
|
| AHU Outdoor Air Minimum Flow is Too Low |
|
|
|
| AHU Return CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
|
| AHU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
|
| AHU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| AHU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
| AHU Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
|
| AHU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
|
| AHU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| AHU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
| FCU A Window is Open While Unoccupied | not applicable | not applicable |
|
| FCU Heating or Cooling While a Window is Open | not applicable |
|
|
| FCU High Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| FCU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
|
| FCU Low Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| FCU Simultaneously Heating and Cooling | not applicable |
|
|
| FCU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| FCU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
| RTU Constantly Running | not applicable | not applicable |
|
| RTU High Discharge Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU High Return Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU High Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU Humidity Setpoint is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
not applicable | not applicable |
| RTU Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
|
| RTU Low Discharge Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU Low Return Air Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU Low Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| RTU Mechanically Cooling without using Economizer |
|
|
|
| RTU Not Running when Occupied | not applicable | not applicable |
|
| RTU Return CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
|
| RTU Return Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
|
| RTU Return Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| RTU Return Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
| RTU Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
|
| RTU Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
|
|
| RTU Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| RTU Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
| VAV High Flow |
|
|
|
| VAV High Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| VAV Insufficient Flow Capacity |
|
|
|
| VAV Insufficient Heating Capacity |
|
|
|
| VAV Low Flow |
|
|
|
| VAV Low Zone Temperature |
|
|
|
| VAV Zone CO2 Level is Too High |
|
|
|
| VAV Zone Humidity is Outside of Comfort Limits |
|
not applicable |
|
| VAV Zone Temperature Cooling Setpoint is Too Low |
|
not applicable |
|
| VAV Zone Temperature Heating Setpoint is Too High |
|
not applicable |
|
How does Fault Triage charting differ from Trends or from a Trend Study?
The difference between Fault Triage charting and trend extensions or trend studies relates to binning and the frequency of the fault generation. While trend extensions and trend studies are exact, the Fault Triage charts data points have a certain tolerance of +/- five minutes. This is mainly due to binning. Sample data for faults are binned in five minute intervals. Fault start and end intervals only occur every 15 minutes on the hour. Utilize trend extensions and trend studies for greater accuracy if needed.
How is the data required for fault evaluation acquired?
Fault evaluation is based on polling, as trend extensions are not required. After polling, the data is binned in five minute bins.
How is the data required for Fault Manager stored?
The Metasys Value database stores a running seven days’ worth of point values and statuses.
How frequently is data evaluated for faults? How frequently are faults created?
This occurs every 60 minutes on the hour. Faults are created based on a 15 minute interval.
Is the Fault Manager supported on all devices?
No, the Fault Manager is only supported on desktop and tablets.
